3. Physics-Informed Deep Learning & Harmonization
Project: Image Harmonization & Material Decomposition
Medical images from different scanners often vary in texture and noise, complicating diagnosis. I developed Physics-Informed Deep Neural Networks that harmonize these images, making a scan from Scanner A look quantitatively identical to Scanner B.
- Generalizability: Unlike standard "black-box" AI, I injected physics constraints (noise power spectra, modulation transfer functions) into the training process and model architecture. This ensured the model learned the underlying physics of image formation, not just dataset correlations.
- Material Decomposition: Extended this work to spectral CT, using Deep Learning to accurately decompose images into their constituent materials (iodine, water, bone) for advanced diagnostics.
Relevant Publications:
- Mojtaba Zarei, et al., "A truth-based primal-dual learning approach to reconstruct CT images utilizing the virtual imaging trial platform," SPIE Medical Imaging, 2022.
- J.H. Valand, Mojtaba Zarei, ... et al., "Truth-Based Physics Informed Estimation of Material Composition in Spectral CT," AAPM, 2024.
- S.J. Xia, Mojtaba Zarei, ... et al., "Evaluation of unified harmonization of CT images across multiple tasks: A step towards AI generalizability," Medical Physics, 2025.
- Mojtaba Zarei, et al., "The role of harmonization: a systematic analysis of various task-based scenarios"
- Mojtaba Zarei, et al., "A probabilistic conditional adversarial neural network to reduce imaging variation in radiography," SPIE Medical Imaging (Best Poster Award), 2021.
- Mojtaba Zarei, et al., "A physics-informed deep neural network for harmonization of CT images"
- Mojtaba Zarei, et al., "Harmonizing CT images via physics-based deep neural networks"
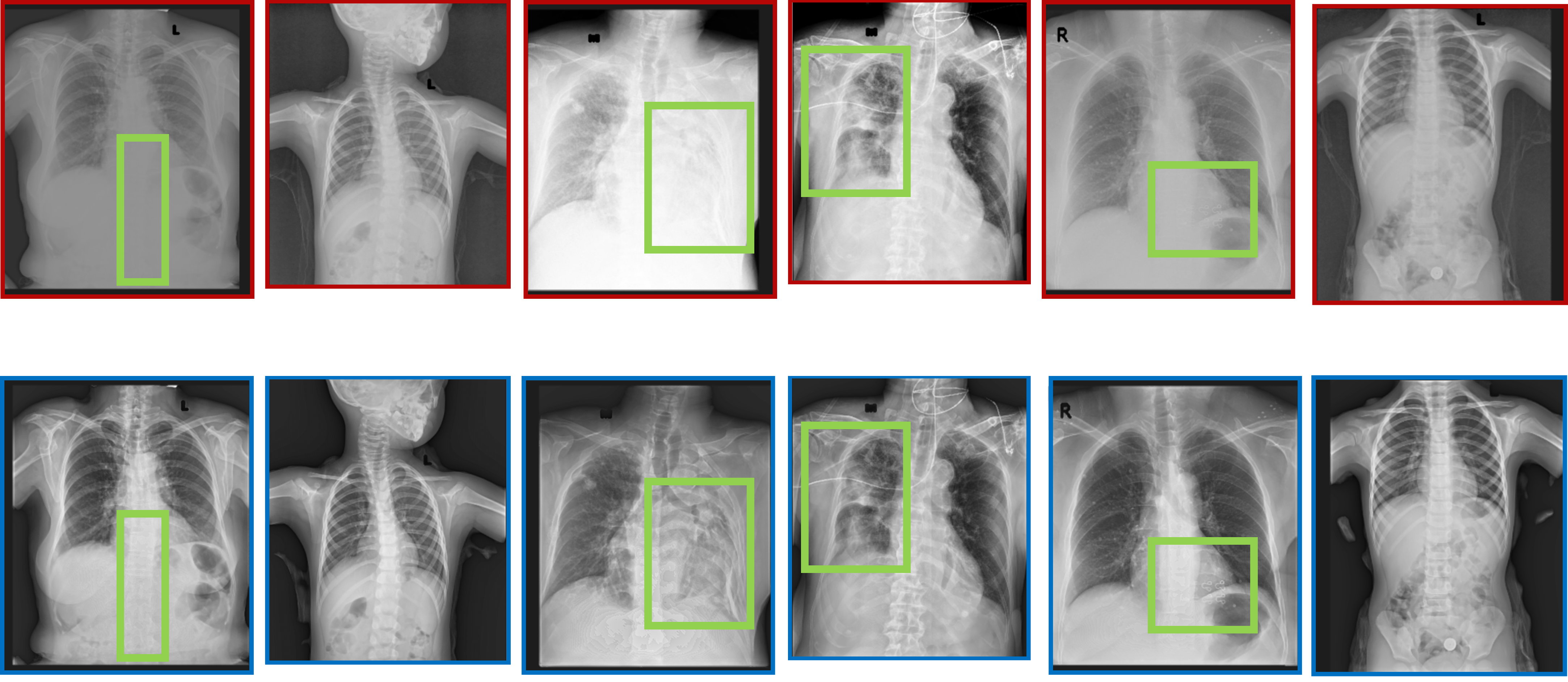
Figure: Comparison of clinical harmonized and non-harmonized CXRs images generated by a physics-informed GAN trained solely on digital twin data.
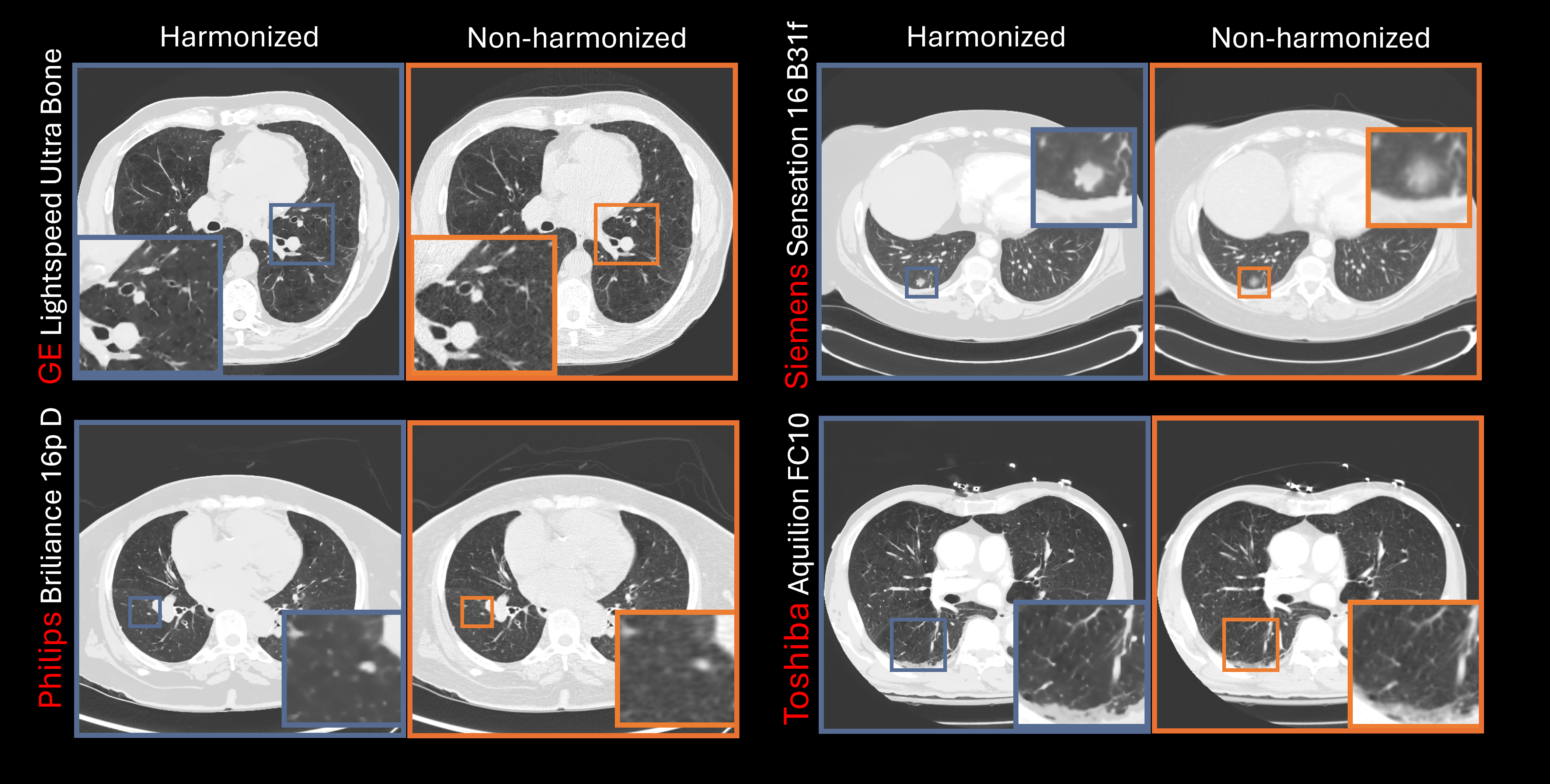
Figure: Comparison of clinical harmonized and non-harmonized CT images generated by a physics-informed GAN trained solely on digital twin data.
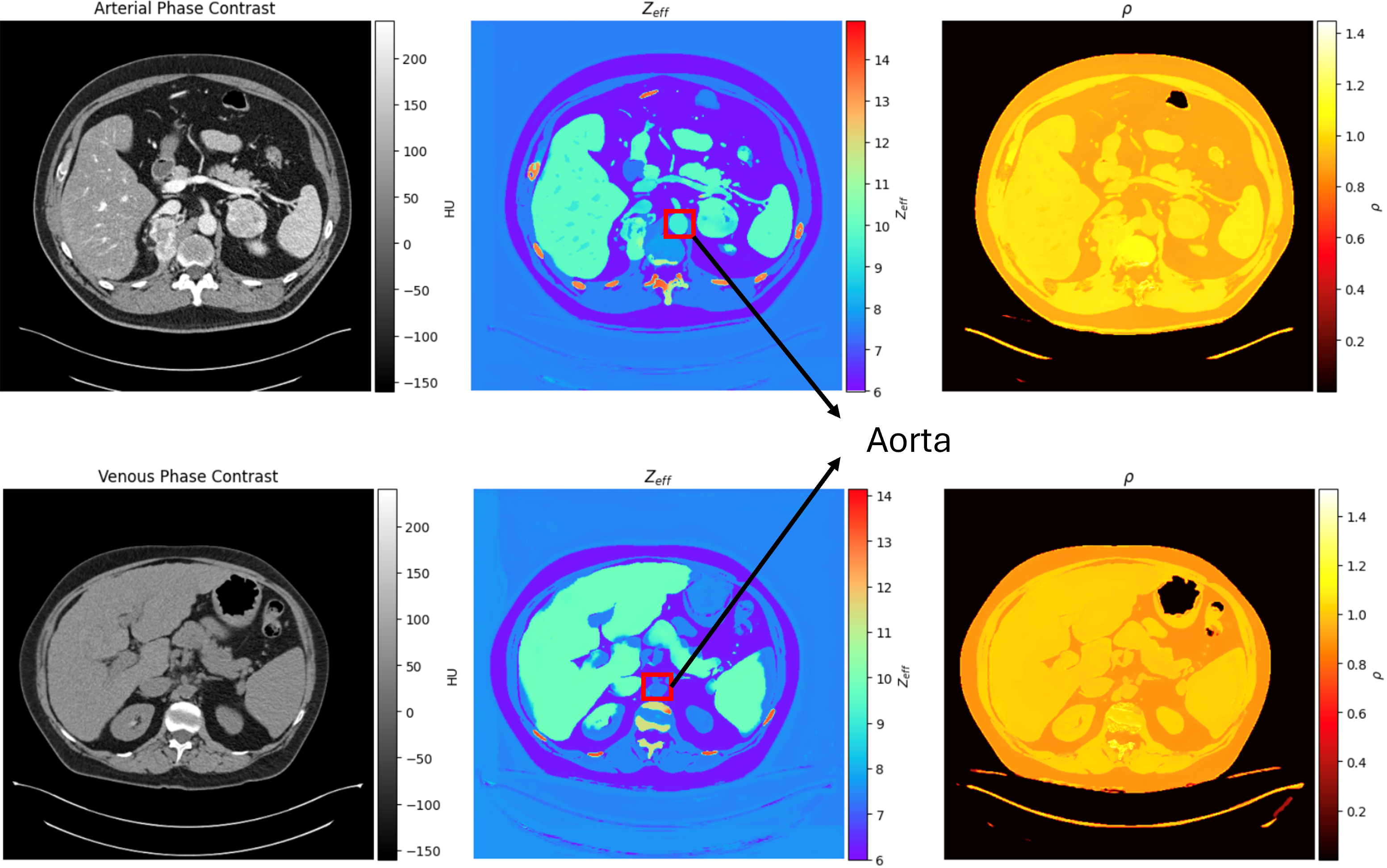
Figure: Clinical material decomposition images from spectral CT generated using a physics-informed GAN trained exclusively on digital twin data.